FKBP
The FK506 binding proteins (FKBP) form a family of PPIases structurally unrelated to cyclophilins. The name of these proteins originates from the high affinity of the prototypic human FKBP12 to the peptidomacrolide FK506.
FKBP are ubiquitously expressed and highly conserved through evolution. FKBPs have a typical architecture with a four- to six-stranded antiparallel sheet wrapped around a short helix.
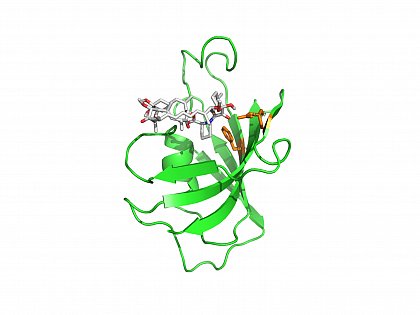
Crystal structure of human FKBP12 in complex with the inhibitor rapamycin. (PDB ID:1FKB, FKBP12/rapamycin) orange: Asp37, Phe99 in the PPIase active site of FKBP12. Van Duyne, G.D., et al. (1991) J.Am.Chem.Soc. 113: 7433
In humans, sixteen FKBP isoenzymes of different molecular masses have been described at present exhibiting specific subcellular localizations. Six human FKBPs are targeted to the ER. The most abundant human FKBP is the cytoplasmic single domain FKBP12 which appears to exhibit distinct cellular functions such as the regulation of two intracellular calcium release channels, the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and ryanodine receptor. In mammals, FKBP12 is essential, the majority of FKBP12 deficient mice die during embryonic life, exhibiting severe cardiac defects.
In addition to the single domain FKBPs, there are several multidomain FKBP members, where the FKBP domain of about 100 amino acids is supplemented by domains of different functionality. Several multidomain FKBP comprise up to four FKBP domains within the same polypeptide chain. In humans, accessory domains of FKBP include the EF hand Ca2+ binding domain or the TPR protein interaction domain.
The TPR domains of FKBP51 and FKBP52 mediate binding of the proteins to Hsp90 organized in steroid receptor complexes. These PPIases contribute to the regulation of steroid hormone receptor signaling, like maturation of receptors, hormone binding and receptor translocation to the nucleus.
Similar as in the case of cyclophilins, formation of a complex between FKBP12 and its inhibitors FK506 or rapamycin mediates clinical immunosuppression important for prevention of organ rejection in transplantation.





